Textbook Question
What mass of HI must be present in 0.250 L of solution to obtain a solution with each pH value?
a. pH = 1.25 b. pH = 1.75 c. pH = 2.85

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
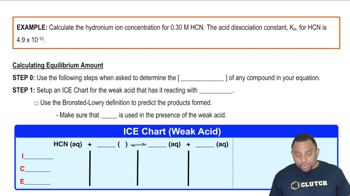
What mass of HI must be present in 0.250 L of solution to obtain a solution with each pH value?
a. pH = 1.25 b. pH = 1.75 c. pH = 2.85
What mass of HClO4 must be present in 0.500 L of solution to obtain a solution with each pH value? a. pH = 2.50 b. pH = 1.50 c. pH = 0.50
What is the pH of a solution in which 224 mL of HCl(g), measured at 27.2 °C and 1.02 atm, is dissolved in 1.5 L of aqueous solution?
Determine the [H3O+] and pH of a 0.100 M solution of benzoic acid.
Determine the [H3O+] and pH of a 0.200 M solution of formic acid.
Determine the pH of an HNO2 solution of each concentration. In which cases can you not make the simplifying assumption that x is small? a. 0.500 M b. 0.100 M c. 0.0100 M