Textbook Question
Pick the stronger base from each pair. a. F– or Cl– b. NO2– or NO3–

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance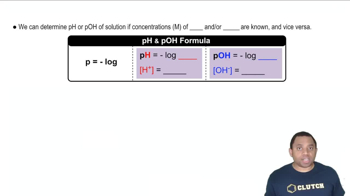


Pick the stronger base from each pair. a. F– or Cl– b. NO2– or NO3–
Pick the stronger base from each pair. c. F– or ClO–
Calculate [H3O+] and [OH–] for each solution at 25 °C. a. pH = 8.55
Calculate [H3O+] and [OH–] for each solution at 25 °C. b. pH = 11.23 c. pH = 2.87