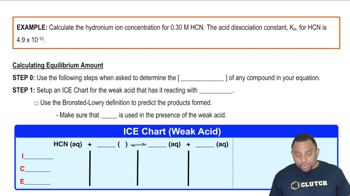
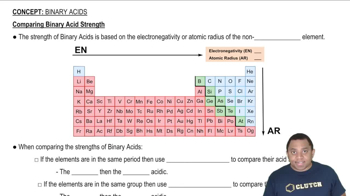
Carbon dioxide dissolves in water according to the equations:
CO2(g) + H2O(l) ⇌ H2CO3(aq)
H2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ HCO3–(aq) + H3O+(aq)
Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere have increased about 20% over the last century. Given that Earth's oceans are exposed to atmospheric carbon dioxide, what effect might the increased CO2 be having on the pH of the world's oceans? What effect might this change be having on the limestone structures (primarily CaCO3) of coral reefs and marine shells?