Textbook Question
Identify each substance as an acid or a base and write a chemical equation showing how it is an acid or a base according to the Arrhenius definition. a. HNO3(aq) b. NH4+(aq) d. HC2H3O2(aq)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
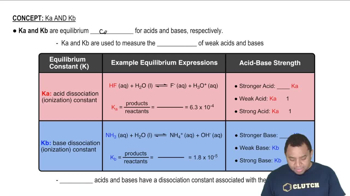

Identify each substance as an acid or a base and write a chemical equation showing how it is an acid or a base according to the Arrhenius definition. a. HNO3(aq) b. NH4+(aq) d. HC2H3O2(aq)
Identify each substance as an acid or a base and write a chemical equation showing how it is an acid or a base according to the Arrhenius definition. c. KOH(aq)