Textbook Question
Calculate Kc for each reaction.
b. CH4(g) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO(g) + 3 H2(g) Kp = 7.7x1024 (at 298 K)
c. I2(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ 2 ICl(g) Kp = 81.9 (at 298 K)
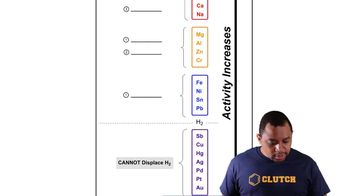
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
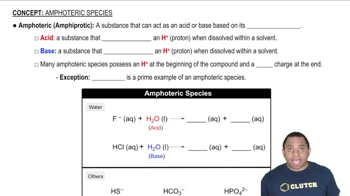
Calculate Kc for each reaction.
b. CH4(g) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO(g) + 3 H2(g) Kp = 7.7x1024 (at 298 K)
c. I2(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ 2 ICl(g) Kp = 81.9 (at 298 K)
Calculate Kp for each reaction. a. N2O4(g) ⇌ 2 NO2(g) Kc = 5.9⨉10-3 (at 298 K)
Calculate Kp for each reaction.
b. N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ⇌ 2 NH3(g) Kc = 3.7⨉108 (at 298 K)
c. N2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2 NO(g) Kc = 4.10⨉10-31 (at 298 K)