Textbook Question
Consider the reaction:
2 HBr (g) → H2 (g) + Br2 (g)
a. Express the rate of the reaction in terms of the change in concentration of each of the reactants and products.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


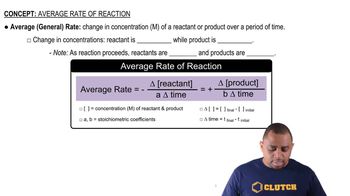
Consider the reaction:
2 HBr (g) → H2 (g) + Br2 (g)
a. Express the rate of the reaction in terms of the change in concentration of each of the reactants and products.
Consider the reaction:
2 HBr (g) → H2 (g) + Br2 (g)
b. In the first 25.0 s of this reaction, the concentration of HBr dropped from 0.600 M to 0.512 M. Calculate the average rate of the reaction during this time interval.
Consider the reaction: 2 N2O( g) → 2 N2(g) + O2(g) a. Express the rate of the reaction in terms of the change in concentration of each of the reactants and products.
For the reaction 2 A(g) + B(g) → 3 C(g), a. Determine the expression for the rate of the reaction in terms of the change in concentration of each of the reactants and products.