Textbook Question
Classify each of the following as a component of a silicate ceramic, an oxide ceramic, or a nonoxide ceramic. a. B4C

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
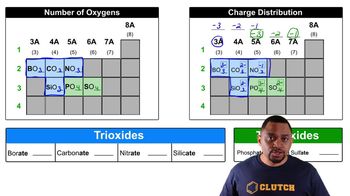
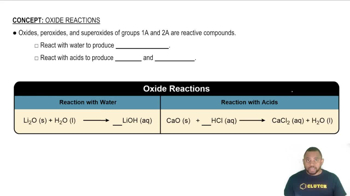
Classify each of the following as a component of a silicate ceramic, an oxide ceramic, or a nonoxide ceramic. a. B4C
Classify each of the following as a component of a silicate ceramic, an oxide ceramic, or a nonoxide ceramic. b. Mg2SiO4
Classify each of the following as a component of a silicate ceramic, an oxide ceramic, or a nonoxide ceramic. c. MoSi2