Textbook Question
Tell whether the free-energy changes, ΔG, for the processes listed in Problem 9.127 are likely to be positive, negative, or zero.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

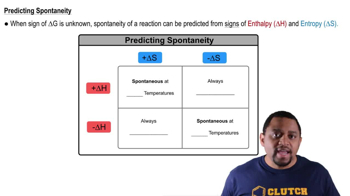
Tell whether the free-energy changes, ΔG, for the processes listed in Problem 9.127 are likely to be positive, negative, or zero.
Ethyl alcohol has ΔHfusion = 5.02 kJ/mol and melts at - 114.1 °C. What is the value of ΔSfusion for ethyl alcohol?