Textbook Question
Which of the following molecules has a central atom with sp3 hybridization? (LO 8.4) (a) PCl5 (b) OF2 (c) CO2 (d) SF4

 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure Problem 9
Problem 9
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

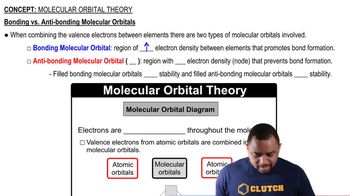
Three of the following molecular models have a tetrahedral central atom, and one does not. Which is the odd one? (There may be a 'hidden' atom directly behind a visible atom in some cases.) (a)
(b)
(c)
(d)