Carbon monoxide is produced by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels. (b) Do you expect CO to be paramagnetic or diamagnetic?

 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
Ch.8 - Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure Problem 111
Problem 111In the cyanate ion, OCN-, carbon is the central atom.(d) Which hybrid orbitals are used by the C atom, and how many p bonds does the C atom form?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Hybridization

Bonding and p Bonds
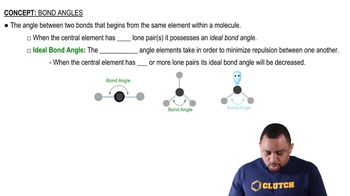
Lewis Structures

Carbon monoxide is produced by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels. (c) What is the bond order of CO? Does this match the bond order predicted by the electron-dot structure?
Cyclooctatetraene dianion, C8H82-, is an organic ion with the structure shown. Considering only the p bonds and not the s bonds, cyclooctatetraene dianion can be described by the following energy diagrams of its p molecular orbitals:
(a) What is the hybridization of the 8 carbon atoms?
Cyclooctatetraene dianion, C8H82-, is an organic ion with the structure shown. Considering only the p bonds and not the s bonds, cyclooctatetraene dianion can be described by the following energy diagrams of its p molecular orbitals:
(b) Three of the p molecular orbitals are bonding, three are antibonding, and two are nonbonding, meaning that they have the same energy level as isolated p orbitals. Which is which?