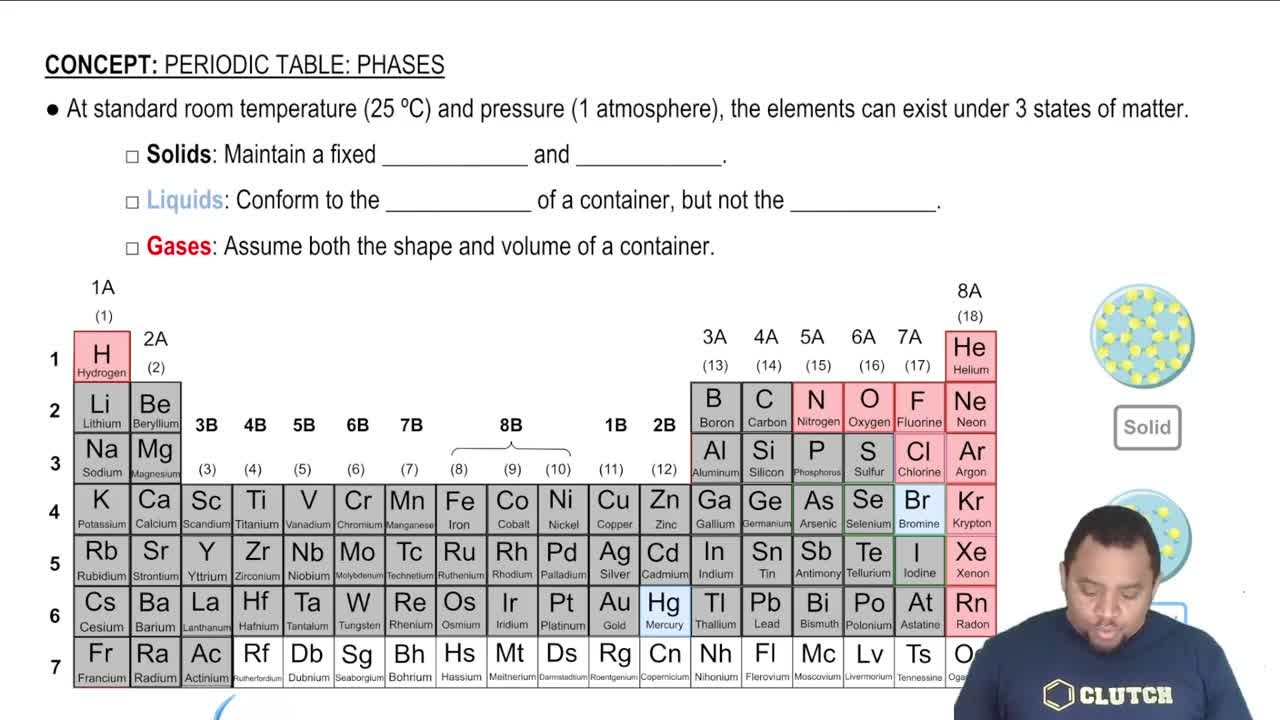
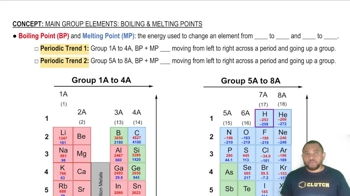
Textbook Question
The graph shows how potential energy changes as a function of the distance between two atoms. (LO 7.2)What is the length of the bond between the two atoms? (a) 3.4 angstroms(b) 3.8 angstroms(c) 6.0 angstroms(d) 8.0 angstroms

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Which of the following pairs represent resonance structures? (LO 7.13) (a)(b)(c)
The structure for the DNA base cytosine is shown.
Which of the following is not a resonance structure of cytosine? (LO 7.13) (a)
(b)
(c)
(d)