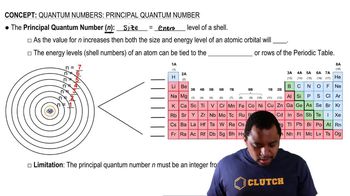
Ionization Energy
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in its gaseous state. It generally increases across a period due to increasing nuclear charge, which attracts electrons more strongly, and decreases down a group as electrons are added to higher energy levels, which are further from the nucleus.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance