Textbook Question
Element X reacts with element Y to give a product containing X3+ ions and Y2-ions. (b) Is element Y likely to be a metal or a nonmetal? Explain.

 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.6 - Ionic Compounds: Periodic Trends and Bonding Theory
Ch.6 - Ionic Compounds: Periodic Trends and Bonding Theory Problem 79
Problem 79 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance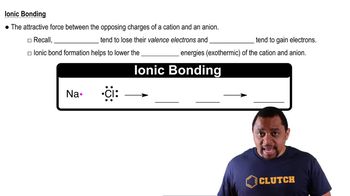
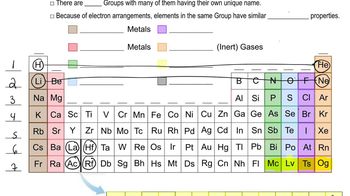
Element X reacts with element Y to give a product containing X3+ ions and Y2-ions. (b) Is element Y likely to be a metal or a nonmetal? Explain.
Element X reacts with element Y to give a product containing X3+ ions and Y2- ions. (c) What is the formula of the product?
Element X reacts with element Y to give a product containing X3+ ions and Y2-ions. (d) In what groups of the periodic table are elements X and Y likely to be found?