Textbook Question
What is the total molar concentration of ions in each of the following solutions, assuming complete dissociation? (a) A 0.750 M solution of K2CO3
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


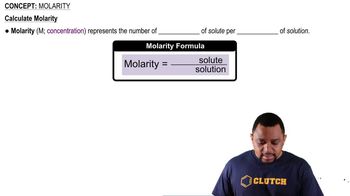
What is the total molar concentration of ions in each of the following solutions, assuming complete dissociation? (a) A 0.750 M solution of K2CO3
What is the total molar concentration of ions in each of the following solutions, assuming complete dissociation? (b) A 0.355 M solution of AlCl3
What is the total molar concentration of ions in each of the following solutions? (a) A 1.250 M solution of CH3OH