Use the activity series of metals (Table 4.5) to predict the outcome of each of the following reactions. If no reaction occurs, write NR. (a)

Use the activity series of metals (Table 4.5) to predict the outcome of each of the following reactions. If no reaction occurs, write NR. (d)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Activity Series of Metals
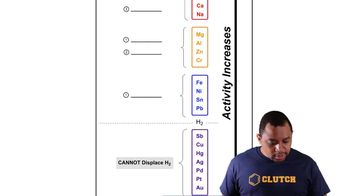
Single Replacement Reactions

Predicting Chemical Reactions

Use the activity series of metals (Table 4.5) to predict the outcome of each of the following reactions. If no reaction occurs, write NR. (b)
Use the activity series of metals (Table 4.5) to predict the outcome of each of the following reactions. If no reaction occurs, write NR. (c)
Neither strontium (Sr) nor antimony (Sb) is shown in the activity series of Table 4.5. Based on their positions in the periodic table, which would you expect to be the better reducing agent? Will the following reaction occur? Explain.
(a) Use the following reactions to arrange the elements A, B, C, and D in order of their decreasing ability as reducing agents:
(b) Which of the following reactions would you expect to occur according to the activity series you established in part (a)?
