Textbook Question
How many grams of solute would you use to prepare the following solutions? (a) 500.0 mL of 1.25 M NaOH

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


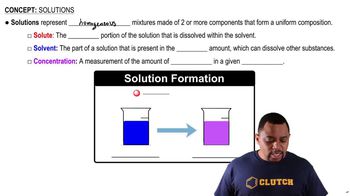
How many grams of solute would you use to prepare the following solutions? (a) 500.0 mL of 1.25 M NaOH
How many grams of solute would you use to prepare the following solutions? (b) 1.50 L of 0.250 M glucose (C6H12O6)