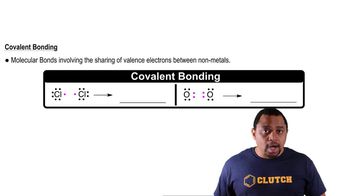
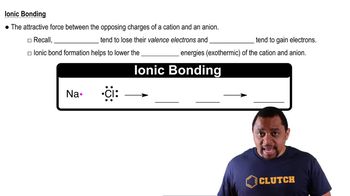
The following diagram represents the reaction of A2 (red spheres) with B2 (blue spheres):
(a) Write a balanced equation for the reaction, and identify the limiting reactant. (b) How many moles of product can be made from 1.0 mol of A2 and 1.0 mol of B2?