Textbook Question
How many grams are in a mole of each of the following substances? (a) Ti

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

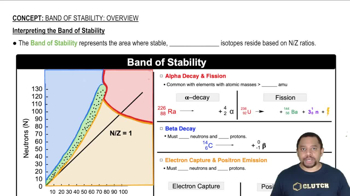
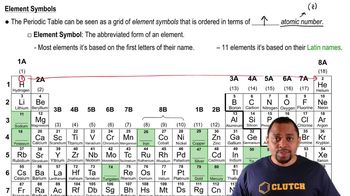
How many grams are in a mole of each of the following substances? (a) Ti
What are the molecular weights of the following pharmaceuticals? (b) C22H27F3O4S (fluticasone, anti-inflammatory)
What are the molecular weights of the following pharmaceuticals? (c) C16H16ClNO2S (clopidogrel, inhibits blood clots)
What are the molecular weights of the following herbicides? (b) C15H22ClNO2 (metolachlor, pre-emergent herbicide)
What are the molecular weights of the following herbicides? (c) C8H6Cl2O3 (dicamba, effective on broadleaf plants