Textbook Question
The molecular weight of an organic compound was found by mass spectrometry to be 70.042 11. Is the sample C5H10, C4H6O, or C3H6N2? Exact masses of elements are: 1.007 825 (1H); 12.000 00 (12C); 14.003 074 (14N); 15.994 915 (16O).

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance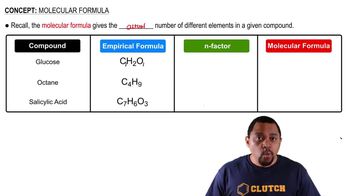
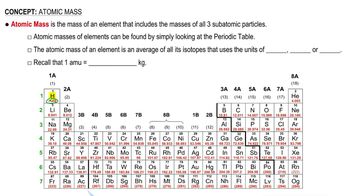

(a) Combustion analysis of 50.0 mg of benzene, a commonly used solvent composed of carbon and hydrogen, gives 34.6 mg of H2O and 169.2 mg of CO2. What is the empirical formula of benzene?
b) Given the mass spectrum of benzene, identify the molecular weight and give the molecular formula.