Textbook Question
Combustion analysis of 45.62 mg of toluene, a commonly used solvent, gives 35.67 mg of H2O and 152.5 mg of CO2. What is the empirical formula of toluene?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance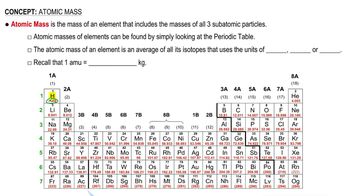

Cytochrome c is an iron-containing enzyme found in the cells of all aerobic organisms. If cytochrome c is 0.43% Fe by mass, what is its minimum molecular weight?