Ch.23 - Organic and Biological Chemistry

Chapter 23, Problem 84
Which of the following compounds are capable of cis–trans isomerism? (a) 1-Hexene (b) 2-Hexene (c) 3-Hexene
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the structural requirement for cis-trans isomerism: a compound must have a double bond with each carbon of the double bond attached to two different groups.
Examine 1-Hexene: The double bond is between the first and second carbon atoms. Since the first carbon is attached to two hydrogen atoms, it cannot have cis-trans isomers.
Examine 2-Hexene: The double bond is between the second and third carbon atoms. Each of these carbons is attached to different groups, allowing for cis-trans isomerism.
Examine 3-Hexene: The double bond is between the third and fourth carbon atoms. Each of these carbons is attached to different groups, allowing for cis-trans isomerism.
Conclude which compounds can exhibit cis-trans isomerism based on the analysis of their structures.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cis-Trans Isomerism
Cis-trans isomerism, also known as geometric isomerism, occurs in compounds with restricted rotation around a double bond or a ring structure. In this type of isomerism, the spatial arrangement of substituents differs, leading to distinct physical and chemical properties. The 'cis' configuration has similar groups on the same side, while the 'trans' configuration has them on opposite sides.
Recommended video:
Guided course
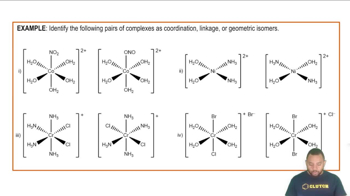
Isomerism in Coordination Complexes Example
Alkenes and Double Bonds
Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C). The presence of this double bond is crucial for cis-trans isomerism, as it restricts the rotation of the carbon atoms involved. The position of substituents around the double bond determines whether the compound can exhibit geometric isomerism.
Recommended video:
Guided course
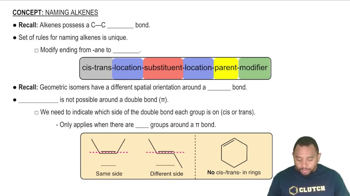
Rules for Naming Alkenes
Substituent Positioning
For a compound to exhibit cis-trans isomerism, it must have two different substituents attached to each carbon of the double bond. If both carbons in the double bond have identical substituents, cis-trans isomerism cannot occur. Therefore, analyzing the structure of the given compounds is essential to determine their capability for geometric isomerism.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Lone Pair Positions
Related Practice
