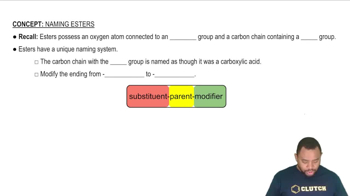
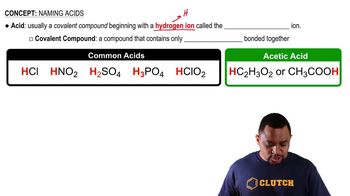
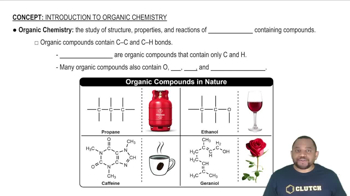
Chemical Structure of Fatty Acids
Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long hydrocarbon chains, which can be saturated or unsaturated. Palmitic acid, specifically, is a saturated fatty acid with a 16-carbon chain, represented as C16H32O2. Understanding the structure of fatty acids is essential for grasping how they interact with alcohols to form esters, as well as their roles in biological systems and industrial applications.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance