Ch.23 - Organic and Biological Chemistry

Chapter 23, Problem 88
Draw the structure of glycerol myristate, a fat made from glycerol and three myristic acid molecules (see Table 23.3).
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the components involved. Glycerol is a triol, meaning it has three hydroxyl (OH) groups. Myristic acid is a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula C14H28O2.
Step 2: Recognize the esterification process. Glycerol myristate is formed by the esterification of glycerol with three myristic acid molecules. Each hydroxyl group of glycerol reacts with the carboxyl group of a myristic acid molecule, releasing water and forming an ester bond.
Step 3: Draw the glycerol backbone. Start by drawing the three-carbon chain of glycerol, with each carbon atom bonded to a hydroxyl group.
Step 4: Attach the myristic acid chains. For each hydroxyl group on the glycerol, draw an ester linkage to a myristic acid chain. This involves connecting the oxygen of the hydroxyl group to the carbonyl carbon of the myristic acid, forming an ester bond.
Step 5: Complete the structure. Ensure that each myristic acid chain is fully drawn, showing the 14-carbon saturated chain attached to the glycerol backbone through the ester linkage.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Glycerol Structure
Glycerol, also known as glycerin, is a simple polyol compound with three hydroxyl (-OH) groups. Its structure consists of a three-carbon chain where each carbon is bonded to a hydroxyl group. This triol nature allows glycerol to act as a backbone for triglycerides, which are formed by esterification with fatty acids.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Resonance Structures
Fatty Acids
Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long hydrocarbon chains, which can be saturated or unsaturated. Myristic acid, specifically, is a saturated fatty acid with a 14-carbon chain. When fatty acids react with glycerol, they form esters, resulting in the formation of triglycerides, which are key components of fats and oils.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Binary Acids
Esterification Reaction
Esterification is a chemical reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, resulting in the formation of an ester and water. In the case of glycerol myristate, glycerol reacts with three myristic acid molecules through this process, leading to the formation of a triglyceride. This reaction is crucial in the synthesis of fats and oils in biological systems.
Recommended video:
Guided course
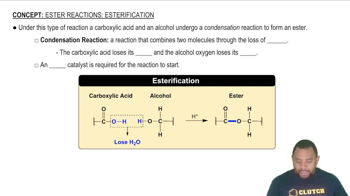
Ester Reactions: Esterification
Related Practice
