Ch.23 - Organic and Biological Chemistry

Chapter 23, Problem 2.142
Butane, the fuel used in disposable lighters, has the formula C4H10. The carbon atoms are connected in the sequence C-C-C-C, and each carbon has four covalent bonds. Draw the structural formula of butane.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in butane from the molecular formula C4H10.
Arrange the four carbon atoms in a straight chain as indicated by the sequence C-C-C-C.
Connect each pair of adjacent carbon atoms with a single covalent bond.
Attach hydrogen atoms to each carbon atom ensuring that each carbon forms four covalent bonds. The two end carbon atoms will each have three hydrogen atoms, and the two middle carbon atoms will each have two hydrogen atoms.
Check the structure to ensure that all valency requirements are met and that the total number of hydrogen atoms equals ten.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are chemical bonds formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. In butane (C4H10), each carbon atom forms four covalent bonds, either with other carbon atoms or with hydrogen atoms. This sharing of electrons allows the atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration, which is essential for the molecule's structure.
Recommended video:
Guided course
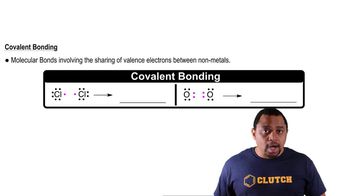
Chemical Bonds
Structural Formula
The structural formula of a compound represents the arrangement of atoms within the molecule, showing how the atoms are connected. For butane, the structural formula illustrates the linear arrangement of four carbon atoms (C-C-C-C) and the associated hydrogen atoms. This visual representation is crucial for understanding the molecule's geometry and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Guided course
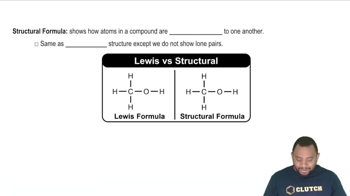
Structural Formula
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Butane is a type of hydrocarbon known as an alkane, characterized by single bonds between carbon atoms. Understanding hydrocarbons is fundamental in organic chemistry, as they serve as the building blocks for more complex molecules and are significant in various applications, including fuels.
Recommended video:
Guided course
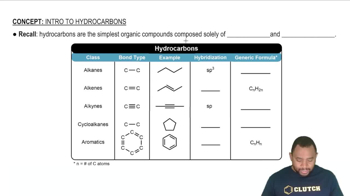
Intro To Hydrocarbons
Related Practice
