Textbook Question
What is a nonstoichiometric compound? Give an example, and account for its lack of stoichiometry in terms of structure.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

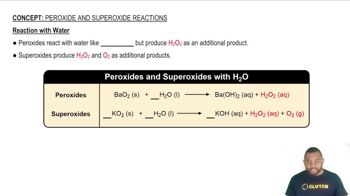
What is a nonstoichiometric compound? Give an example, and account for its lack of stoichiometry in terms of structure.
Explain why the hydrogen atoms in interstitial hydrides are mobile.
Look at the properties of the alkali metals summarized in
Table 22.2, and predict reasonable values for the melting
point, boiling point, density, and atomic radius of francium.