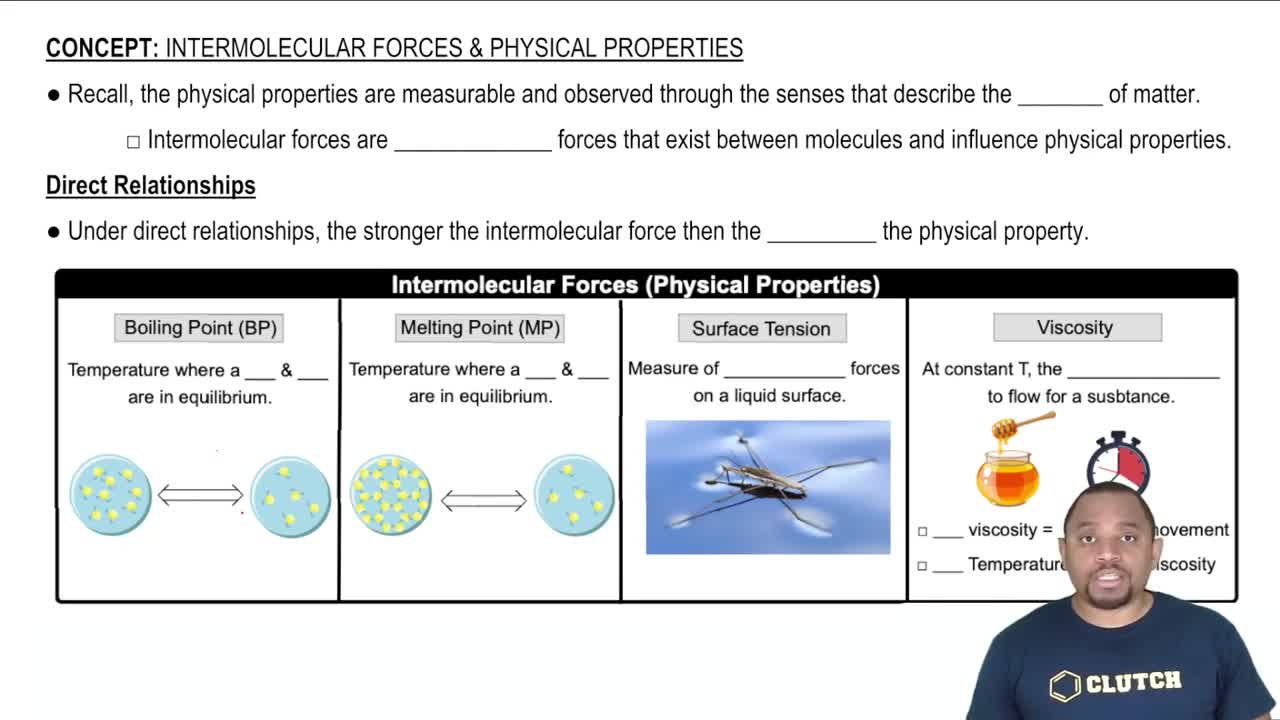
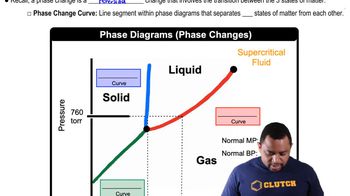
Temperature Effects on Liquids
Temperature significantly impacts the physical properties of liquids, including viscosity. As temperature increases, the kinetic energy of molecules rises, leading to reduced intermolecular forces and typically lower viscosity. However, at certain temperatures, such as the transition points in sulfur, structural changes or phase transitions can occur, resulting in unexpected viscosity behavior.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance