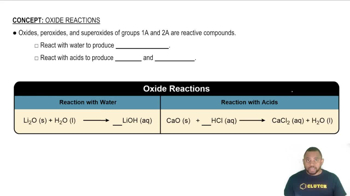
Textbook Question
Write chemical equations for the reaction of calcium with the following substances, making sure that the numbers and kinds of atoms are the same on both sides of the equations. If no reaction occurs, write N.R.
(d) O2

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance