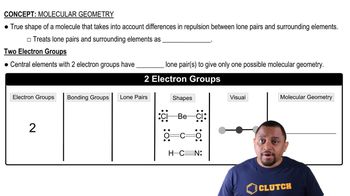
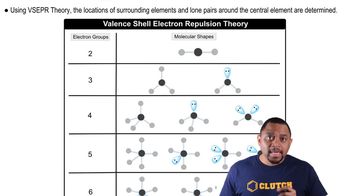
Electron-Dot Structure
The electron-dot structure, also known as the Lewis structure, represents the valence electrons of atoms within a molecule. It uses dots to depict the electrons and lines to indicate bonds between atoms. For XeO3, the structure helps visualize how xenon and oxygen atoms are bonded and the distribution of lone pairs, which is crucial for understanding molecular geometry.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance