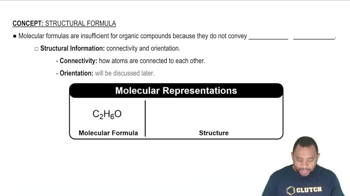
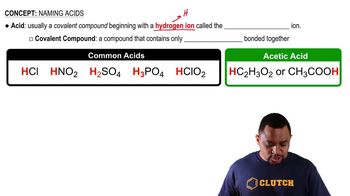
Molecular Structure
Molecular structure refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It includes the types of bonds (single, double, or triple) and the angles between them, which influence the molecule's properties and reactivity. Understanding molecular structure is essential for predicting how molecules will interact in chemical reactions.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance