Textbook Question
BF3 reacts with F- to give BF4-, but AlF3 reacts with F- to give AlF63-. Explain.
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

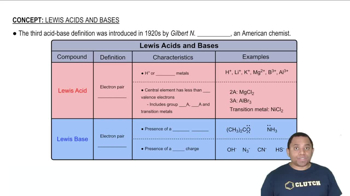
BF3 reacts with F- to give BF4-, but AlF3 reacts with F- to give AlF63-. Explain.
Which of the following elements is the best conductor of electricity? (LO 22.1)
(a) N (b) As
(c) P (d) Bi
Which element will react most vigorously with water, and what is the reaction that occurs?
(a) Lithium; 2 Li(s) + 2 H2O(l) → 2 Li+(aq) + 2 H–(aq) + H2O2(aq)
(b) Potassium; 2 K(s) + 2 H2O(l) → 2 K+(aq) + 2 OH–(aq) + H2(g)
(c) Magnesium; Mg(s) + 2 H2O(l) → Mg2+(aq) + 2 OH–(aq) + H2(g)
(d) Barium; Ba(s) + 2 H2O(l) → Ba2+(aq) + 2 H–(aq) + H2O2(aq)