Textbook Question
Account for each of the following observations.
(a) H2SO4 is a stronger acid than H2SO3.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance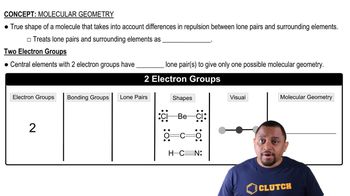
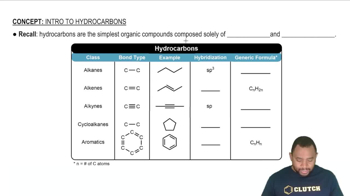
Account for each of the following observations.
(a) H2SO4 is a stronger acid than H2SO3.
Account for each of the following observations.
b. SF4 exists, but OF4 does not.
Little is known about the chemistry of astatine (At) from direct observation, but reasonable predictions can be made.
(a) Is astatine likely to be a gas, a liquid, or a solid?