
The oxalate ion is a bidentate ligand as indicated in Figure 21.8. Would you expect the carbonate ion to be a monodentate or bidentate ligand? Explain your reasoning.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
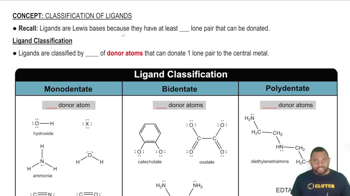
Ligands

Bidentate vs. Monodentate Ligands
Structure of Carbonate Ion

Draw a crystal field energy-level diagram for the 3d orbitals of titanium in [Ti(H2O)6]3+]. Indicate the crystal field splitting, and explain why is [Ti(H2O)6]3+] colored.
Draw the three possible diastereoisomers of the triethylenetetramine complex [Co(trend)Cl2]+. Abbreviate the flexible tetradentate trien ligand H2NCH2CH2NHCH2CH2NHCH2CH2NH2 as . Which of the isomers can exist as a pair of enantiomers?
What is the oxidation state of the metal in each of the complexes?
a. AgCl2–
b. [Cr(H2O)5Cl]2+
c. [Co(NCS)4]2–
d. [ZrF8]4–
e. [Fe(EDTA)(H2O)]–
What is the electron configuration of Co2+ and how many unpaired electrons are in the free transition metal ion?
(a) [Ar]3d54s2; 5 unpaired electrons
(b) [Ar]3d54s2; 1 unpaired electron
(c) [Ar]3d7; 3 unpaired electrons
(d) [Ar]3d7; 1 unpaired electron
