What is the coordination number of the metal in each of the following complexes?
(a) AgCl2-
(b) [Cr(H2O)5Cl]2+
(c) [Co(NCS)4]2-

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


What is the coordination number of the metal in each of the following complexes?
(a) AgCl2-
(b) [Cr(H2O)5Cl]2+
(c) [Co(NCS)4]2-
What is the coordination number of the metal in each of the following complexes?
(d) [ZrF8]4-
(e) [Fe(EDTA)(H2O)]-
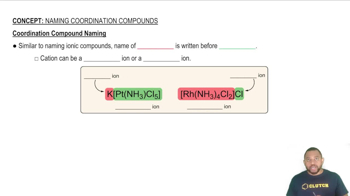
Identify the oxidation state of the metal in each of the following compounds.
(a) (NH4)3[RhCl6]
(b) [Cr(NH3)4(SCN)2]Br
(c) [Cu(en)2]SO4
(d) Na2[Mn(EDTA)]
What is the formula, including the charge, for each of the following complexes?
(a) An iridium(III) complex with three ammonia and three chloride ligands
(b) A chromium(III) complex with two water and two oxalate ligands
(c) A platinum(IV) complex with two ethylenediamine and two thiocyanate ligands
What is the formula, including the charge, for each of the following complexes?
(a) An iron(III) complex with six water ligands
(b) A nickel(II) complex with two ethylenediamine and two bromide ligands
(c) A platinum(II) complex with two chloride and two ammonia ligands