Textbook Question
Give systematic names for the following compounds: (f) (NH4)2SO4
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

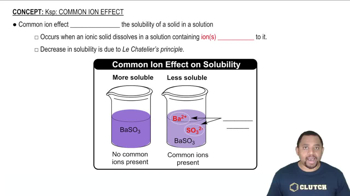
Give systematic names for the following compounds: (f) (NH4)2SO4
Name the following ions: (a) Ba2+ (b) Cs+ (c) V3+ (d) HCO3- (e) NH4 (f) Ni2+ (g) NO2- (h) ClO2- i) Mn2+ (j) ClO4-
What are the formulas of the compounds formed from the following ions? (a) Ca2+ and Br- (b) Ca2+ and SO42- (c) Al3+ and SO42-