Textbook Question
What particle is produced in each of the following decay reactions? (b)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
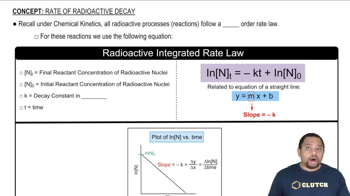
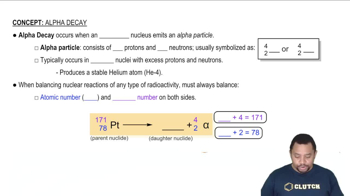
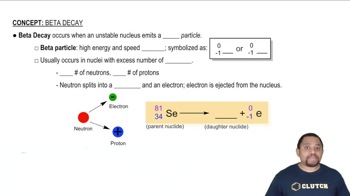
What particle is produced in each of the following decay reactions? (b)
What particle is produced in each of the following decay reactions? (c)
What particle is produced in each of the following decay reactions? (a)
What particle is produced in each of the following decay reactions? (c)
Write balanced nuclear equations for the following processes. (a) Alpha emission of 162Re
Write balanced nuclear equations for the following processes. (b) Electron capture of 138Sm