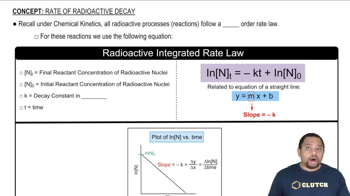
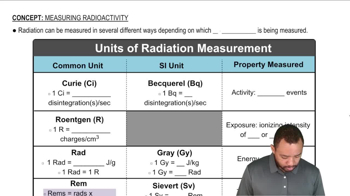
Half-Life
The half-life of a radioactive isotope is the time it takes for half of the original amount of the isotope to decay into another element or isotope. For ²²⁶Ra, the half-life is 1600 years, meaning that after this period, only half of the original amount will remain. This concept is essential for determining the remaining quantity of a radioactive substance over time.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance