The silver oxide–zinc battery used in watches delivers a voltage of 1.60 V. Calculate the free-energy change (in kilo-joules) for the cell reaction
Ch.19 - Electrochemistry

Chapter 19, Problem 19.67
How are standard reduction potentials defined?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Standard reduction potentials are defined as the voltage associated with a reduction reaction at an electrode when all solutes are at a concentration of 1 M, all gases are at a pressure of 1 atm, and the temperature is 25°C (298 K).
These potentials are measured under standard conditions and are used to predict the direction of electron flow in electrochemical cells.
The standard reduction potential is denoted by E° and is measured in volts (V).
A positive E° value indicates a greater tendency for the species to gain electrons and be reduced, while a negative E° value indicates a lesser tendency.
Standard reduction potentials are typically listed in tables, with the reduction of hydrogen ions to hydrogen gas (2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → H₂) assigned a potential of 0.00 V as a reference point.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Standard Reduction Potential
Standard reduction potential (E°) is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to gain electrons and be reduced. It is defined under standard conditions (1 M concentration, 1 atm pressure, and 25°C) and is measured in volts. A higher E° value indicates a greater likelihood of reduction occurring, making it a crucial parameter in electrochemistry.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Standard Reduction Potentials
Electrochemical Cells
Electrochemical cells are devices that convert chemical energy into electrical energy through redox reactions. They consist of two electrodes: an anode (where oxidation occurs) and a cathode (where reduction occurs). The standard reduction potentials of the half-reactions at these electrodes determine the overall cell potential and the direction of electron flow.
Recommended video:
Guided course
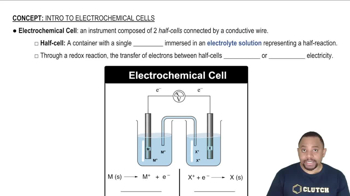
Electrochemical Cells
Nernst Equation
The Nernst equation relates the standard reduction potential of a half-cell to the concentrations of the reactants and products involved in the redox reaction. It allows for the calculation of the cell potential under non-standard conditions, providing insight into how changes in concentration affect the driving force of the reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

The Nernst Equation
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Calculate the standard cell potential and the standard free-energy change (in kilojoules) for the reaction below. (See Appendix D for standard reduction potentials.) <QUESTION REFERENCES APPENDIX D>
Textbook Question
Consider a Daniell cell with 1.0 M ion concentrations: Does the cell voltage increase, decrease, or remain the same when each of the following changes is made? Explain. (a) Write a balanced equation for each cell reaction.
Textbook Question
Sketch a cell with inert electrodes suitable for electrolysis of aqueous CuBr2. (b) Indicate the direction of electron and ion flow.
17
views
Textbook Question
Porous pellets of TiO2 can be reduced to titanium metal at the cathode of an electrochemical cell containing molten CaCl2 as the electrolyte. When the TiO2 is reduced, the O2-ions dis-solve in the CaCl2 and are subsequently oxidized to O2 gas at the anode. This approach may be the basis for a less expensive process than the one currently used for producing titanium.
(a) Label the anode and cathode, and indicate the signs of the electrodes.
