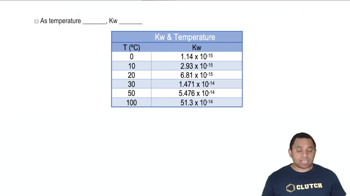
Temperature Dependence of K
The value of the equilibrium constant (K) is temperature-dependent, meaning it can change with variations in temperature. For exothermic reactions, increasing temperature typically decreases K, while for endothermic reactions, increasing temperature usually increases K. Understanding this relationship is crucial for calculating K at different temperatures.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance