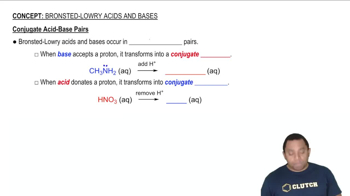
Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Conjugate acid-base pairs consist of an acid and its corresponding base, which differ by a proton (H+). For example, in the pair HSO4- (acid) and SO42- (base), HSO4- can donate a proton to form SO42-. The choice of conjugate pairs is essential for buffer preparation, as the pKa of the acid should be close to the desired pH for optimal buffering capacity.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance