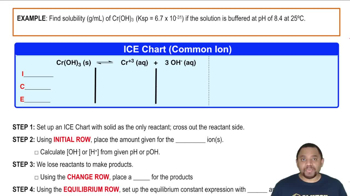
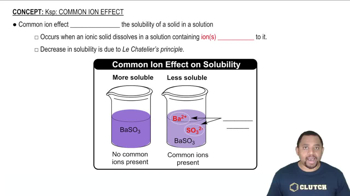
Common Ion Effect
The common ion effect describes how the solubility of a salt decreases in a solution that already contains one of its constituent ions. In acidic solutions, the addition of H+ can influence the solubility of compounds like carbonates, which react with H+ to form soluble species, thus increasing their solubility.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance