Textbook Question
Use Le Châtelier's principle to predict whether the solubility of BaF2 will increase, decrease, or remain the same on addition of each of the following substances. (a) HCl

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


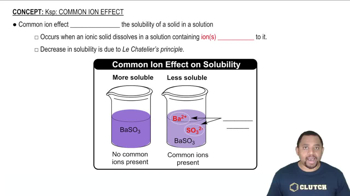
Use Le Châtelier's principle to predict whether the solubility of BaF2 will increase, decrease, or remain the same on addition of each of the following substances. (a) HCl
Use Le Châtelier's principle to predict whether the solubility of BaF2 will increase, decrease, or remain the same on addition of each of the following substances. (b) KF
Use Le Châtelier's principle to predict whether the solubility of BaF2 will increase, decrease, or remain the same on addition of each of the following substances. (c) NaNO3