Textbook Question
Which of the following compounds are more soluble in acidic solution than in pure water? Write a balanced net ionic equation for each dissolution reaction. (b) Fe(OH)3

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

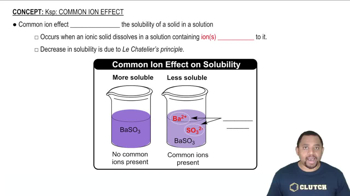

Which of the following compounds are more soluble in acidic solution than in pure water? Write a balanced net ionic equation for each dissolution reaction. (b) Fe(OH)3
Is the solubility of Zn(OH)2 increased, decreased, or unchanged on addition of each of the following substances? Write a balanced net ionic equation for each dissolution reaction. (See Appendix C.6 for formulas of complex ions.) (b) KOH
Is the solubility of Zn(OH)2 increased, decreased, or unchanged on addition of each of the following substances? Write a balanced net ionic equation for each dissolution reaction. (See Appendix C.6 for formulas of complex ions.) (c) NaCN