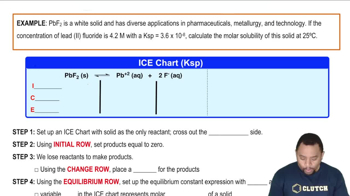
Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)
The solubility product constant (Ksp) is an equilibrium constant that applies to the solubility of sparingly soluble ionic compounds. It is defined as the product of the molar concentrations of the ions, each raised to the power of their coefficients in the balanced equation. For MnS, Ksp = [Mn^2+][S^2-], and knowing Ksp helps in calculating the molar solubility in different conditions.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance