
What is the pH of the mixture before the addition of any base?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
pH Scale

Acid-Base Chemistry
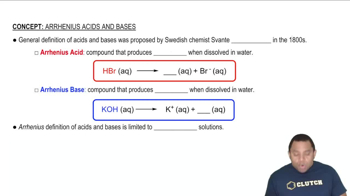
Buffer Solutions

A 40.0 mL sample of a mixture of HCl and H3PO4 was titrated with 0.100 M NaOH. The first equivalence point was reached after 88.0 mL of base, and the second equivalence point was reached after 126.4 mL of base. (a) What is the concentration of H3O+ at the first equivalence point?
A 40.0 mL sample of a mixture of HCl and H3PO4 was titrated with 0.100 M NaOH. The first equivalence point was reached after 88.0 mL of base, and the second equivalence point was reached after 126.4 mL of base. (b) What are the initial concentrations of HCl and H3PO4 in the mixture?
A 40.0 mL sample of a mixture of HCl and H3PO4 was titrated with 0.100 M NaOH. The first equivalence point was reached after 88.0 mL of base, and the second equivalence point was reached after 126.4 mL of base. (c) What percent of the HCl is neutralized at the first equivalence point?
