Textbook Question
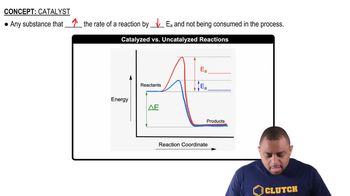
The equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction PCl51g2 ∆ PCl31g2 + Cl21g2 is 3.81 * 102 at 600 K and 2.69 * 103 at 700 K.(b) How are the equilibrium amounts of reactants and products affected by (iii) addition of a catalyst?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance