Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Colligative Properties
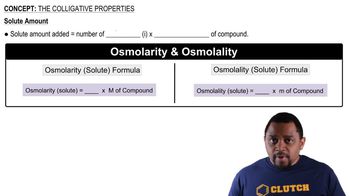
Colligative properties are physical properties of solutions that depend on the number of solute particles in a given amount of solvent, rather than the identity of the solute. These properties include boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and vapor pressure lowering. Understanding these properties is essential for comparing the effects of different solutes on the physical characteristics of solutions.
Recommended video:
Freezing Point Depression
Freezing point depression occurs when a solute is added to a solvent, resulting in a lower freezing point than that of the pure solvent. The extent of freezing point depression is directly proportional to the molality of the solute particles in the solution. In this question, comparing the molalities of sucrose and HNO3 helps determine which solution will have a higher freezing point.
Recommended video:
Freezing Point Depression
Boiling Point Elevation
Boiling point elevation is the phenomenon where the boiling point of a solvent increases when a solute is dissolved in it. This effect is also proportional to the number of solute particles in the solution. In the context of the question, the solution with the greater number of solute particles will exhibit a higher boiling point, which can be assessed by considering the dissociation of HNO3 compared to the non-dissociating sucrose.
Recommended video: