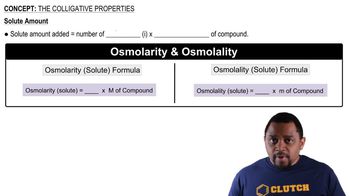
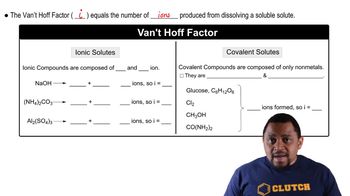
Textbook Question
The following phase diagram shows part of the vapor- pressure curves for a pure liquid (green curve) and a solution of the first liquid with a second volatile liquid (red curve). (a) Is the boiling point of the second liquid higher or lower than that of the first liquid?
1
views