The dissolution of CaCl2(s) in water is exothermic, with ΔHsoln= - 81.3 kJ>mol. If you were to prepare a 1.00 m solution of CaCl2 beginning with water at 25.0 °C, what would the final temperature of the solution be in °C? Assume that the specific heats of both pure H2O and the solution are the same, 4.18 J>1K g2.
Ch.13 - Solutions & Their Properties

Chapter 13, Problem 59
Residues of the herbicide atrazine C8H14ClN5 in water can be detected at concentrations as low as 0.050 mg/L. Express this concentration of atrazine in the following units: (a) Parts per billion (assume a solution density of 1.00 g/mL)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the relationship between milligrams per liter (mg/L) and parts per billion (ppb). Parts per billion is a unit of concentration that is equivalent to micrograms per liter (µg/L) when the density of the solution is 1 g/mL.
Convert the given concentration from milligrams per liter to micrograms per liter. Since 1 mg = 1000 µg, multiply the concentration in mg/L by 1000 to convert it to µg/L.
Recognize that when the density of the solution is 1 g/mL, 1 µg/L is equivalent to 1 ppb. Therefore, the concentration in µg/L is directly equal to the concentration in ppb.
Use the conversion factor to express the concentration in parts per billion. Since the density is 1 g/mL, the concentration in µg/L is the same as the concentration in ppb.
Conclude that the concentration of atrazine in parts per billion is numerically equal to the concentration in micrograms per liter, which you calculated in the previous steps.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Concentration Units
Concentration is a measure of the amount of a substance in a given volume of solution. Common units include milligrams per liter (mg/L), parts per million (ppm), and parts per billion (ppb). Understanding how to convert between these units is essential for accurately expressing the concentration of substances in various contexts, particularly in environmental chemistry.
Recommended video:
Guided course

SI Units
Parts Per Billion (ppb)
Parts per billion (ppb) is a unit of measurement that describes the concentration of a substance in a solution. It indicates how many parts of a substance are present in one billion parts of the total solution. For example, 1 ppb is equivalent to 1 microgram of solute in 1 liter of solution, making it a useful unit for measuring trace contaminants like herbicides in water.
Recommended video:
Guided course
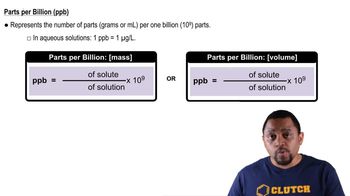
Parts per Billion (ppb)
Density of Water
The density of water is typically assumed to be 1.00 g/mL at standard conditions, which simplifies calculations involving concentrations. This means that 1 liter of water has a mass of approximately 1000 grams. When converting concentrations from mg/L to ppb, this density assumption allows for straightforward conversions, as 1 mg/L is equivalent to 1 ppb in water.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Density via Water Displacement
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Assuming that seawater is an aqueous solution of NaCl, what is its molarity? The density of seawater is 1.025 g/mL at 20 °C, and the NaCl concentration is 3.50 mass %.
Textbook Question
Propranolol 1C16H21NO22, a so-called beta-blocker that is used for treatment of high blood pressure, is effective at a blood plasma concentration of 50 ng/L. Express this concen- tration of propranolol in the following units: (b) Molarity
Textbook Question
Residues of the herbicide atrazine (C8H14ClN5) in water can be detected at concentrations as low as 0.050 µg/L. Express this concentration of atrazine in the following units: (b) Molarity
Textbook Question
How would you prepare each of the following solutions?(c) A solution of methyl alcohol (methanol) and water in which Xmethanol = 0.15 and Xwater = 0.85
