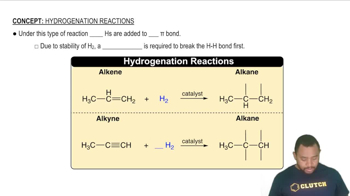
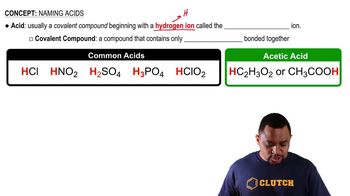
Textbook Question
The following pictures represent solutions of AgCl, which also may contain ions other than Ag+ and Cl- that are not shown. If solution 1 is a saturated solution of AgCl, classify solutions 2–4 as unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated. (1) (2) (3) (4)