Textbook Question
Identify each of the following kinds of packing: (d)
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Identify each of the following kinds of packing: (d)
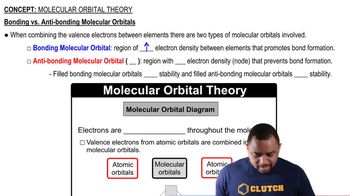
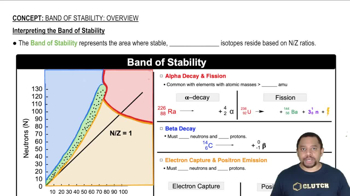
The following diagrams show the electron populations of the bands of MO energy levels for four different materials:
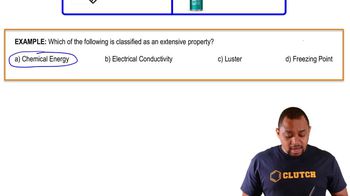
. (c) Tell whether the conductivity of each material increases or decreases when the temperature increases.